Configuring Remote Executor
Overview
This guide will walk you through the process of setting up Remote Executors in your environment, including:
- Understanding Remote Executors and Pools
- Configuration prerequisites
- Creating and managing Executor Pools
- Deploying Remote Executors in your environment
- Assigning Ingestion Sources to Pools
Understanding Remote Executors and Pools
A Remote Executor Pool provides a way to organize and manage your Remote Executors in DataHub. Here's how they work:
- A Remote Executor Pool (or Pool) is a logical grouping of one or more Remote Executors
- Each Remote Executor in a Pool automatically reports its status and health
- Each Ingestion Source can be assigned to a specific Pool
- One Pool can be designated as the Default Pool for new Ingestion Sources
- Multiple Pools can be created for different purposes (e.g., by region, department, or workload type)
Configuration Prerequisites
Before deploying a Remote Executor, ensure you have the following:
DataHub Cloud
- A DataHub User with the Manage Metadata Ingestion Platform privilege
- A DataHub Remote Executor Access Token (generate from Settings > Access Tokens > Generate new token > Remote Executor)
- Your DataHub Cloud URL (e.g.,
<your-company>.acryl.io/gms). NOTE: you MUST include the trailing/gmswhen configuring the executor.
Deployment Environment
- Access to your deployment platform (AWS ECS or Kubernetes)
- Necessary permissions to create resources
Registry Access
- For AWS: Provide your AWS account ID to Acryl
- For Kubernetes: Work with Acryl to set up access to the Remote Executor Docker Image Registry
Creating and Managing Executor Pools
Complete the following steps to create a new Executor Pool from the DataHub Cloud UI:
- Navigate to the Data Sources section on the left sidebar
- Click the Executors tab and click Create

- Configure Pool settings:
- Pool Identifier: A unique identifier for this Pool
- Description: Purpose or details about the Pool
- Default Pool: Optionally set as the Default Pool for new Ingestion Sources

- Click Create to provision the Pool
Deploying Remote Executors in Your Environment
Once you have created an Executor Pool in DataHub Cloud, you are now ready to deploy an Executor within your environment.
Work with Acryl to receive deployment templates specific to your environment (Helm charts, CloudFormation, or Terraform) for deploying Remote Executors in this Pool.
- Amazon ECS
- Kubernetes
Deploy on Amazon ECS
- AWS Account Configuration
To access the private Acryl ECR registry, you'll need to provide your AWS account ID to Acryl. You can securely share your account ID through:
- Your Acryl representative
- A secure secret-sharing service like One Time Secret
This step is required to grant your AWS account access to pull the Remote Executor container image.
- Configure CloudFormation Template
The Acryl Team will provide a Cloudformation Template that you can run to provision an ECS cluster with a single remote ingestion task. It will also provision an AWS role for the task which grants the permissions necessary to read and delete from the private queue created for you, along with reading the secrets you've specified. At minimum, the template requires the following parameters:
Deployment Location (VPC and subnet)
DataHub Personal Access Token
DataHub Cloud URL (e.g.,
<your-company>.acryl.io/gms)Optional: Acryl Remote Executor Version; defaults to latest
Optional parameters:
Source Secrets:
SECRET_NAME=SECRET_ARN(up to 10); separate multiple secrets by comma, e.g.SECRET_NAME_1=SECRET_ARN_1,SECRET_NAME_2,SECRET_ARN_2.Environment Variables:
ENV_VAR_NAME=ENV_VAR_VALUE(up to 10); separate multiple variable by comma, e.g.ENV_VAR_NAME_1=ENV_VAR_VALUE_1,ENV_VAR_NAME_2,ENV_VAR_VALUE_2.
Configuring Secrets enables you to manage ingestion sources from the DataHub UI without storing credentials inside DataHub. Once defined, secrets can be referenced by name inside of your DataHub Ingestion Source configurations using the usual convention: ${SECRET_NAME}.
Deploy Stack
# Using AWS CLI
aws cloudformation create-stack \
--stack-name datahub-remote-executor \
--template-body file://datahub-executor.ecs.template.yaml \
--parameters ParameterKey=... ParameterValue=...Or use the CloudFormation Console
Configure Secrets (Optional)
# Create a secret in AWS Secrets Manager
aws secretsmanager create-secret \
--name my-source-secret \
--secret-string '{"username":"user","password":"pass"}'
Update Amazon ECS Deployment
To update your Remote Executor deployment (e.g., to deploy a new container version or modify configuration), you'll need to update your existing CloudFormation Stack. This process involves re-deploying the CloudFormation template with your updated parameters while preserving your existing resources.
Access CloudFormation
- Navigate to the AWS CloudFormation Console
- Locate and select your Remote Executor stack
- Click the Update button
Update Template
- Select Replace current template
- Choose Upload a template file
- Download the latest Acryl Remote Executor CloudFormation Template
- Upload the template file
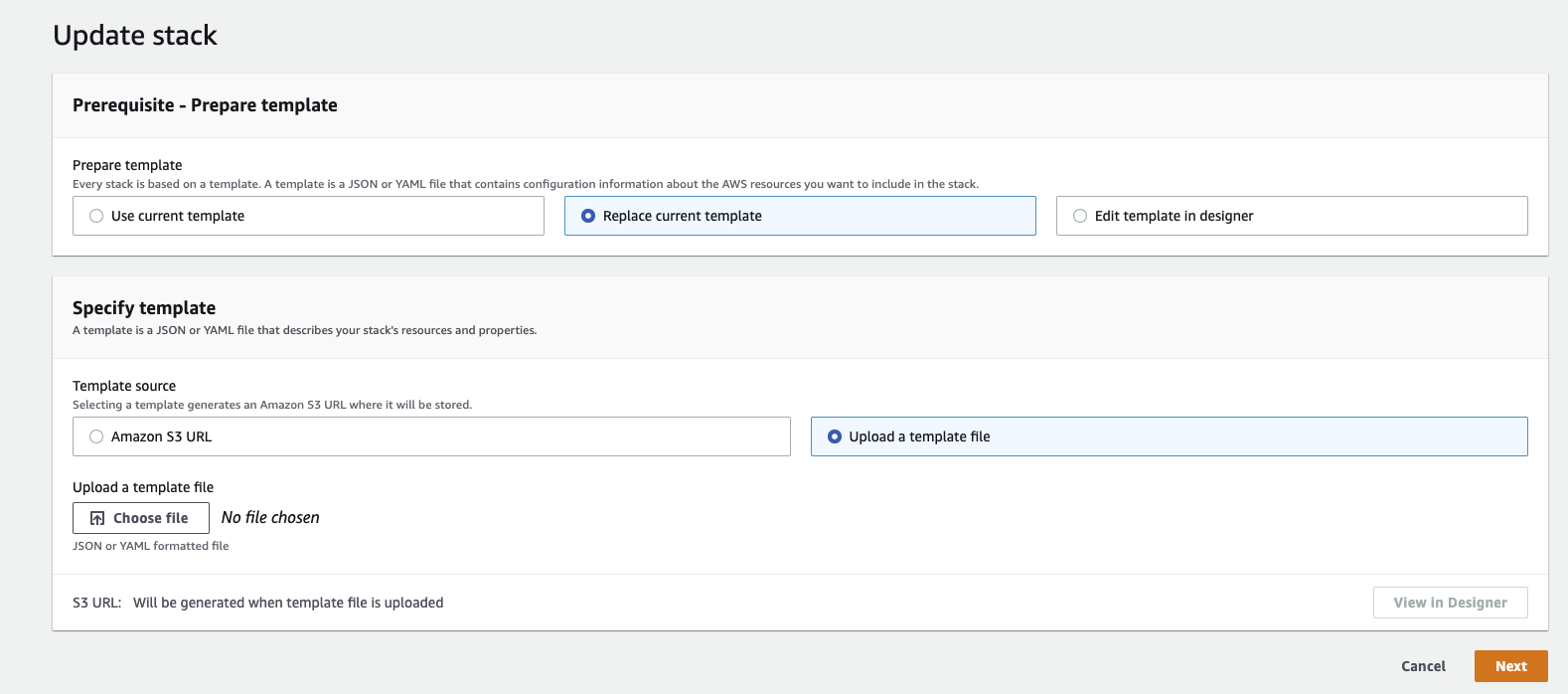
Configure Parameters
- Review and update parameters as needed:
ImageTag: Specify a new version if upgradingDatahubGmsURL: Verify your DataHub URL is correct- Other parameters will retain their previous values unless changed
- Click Next to proceed
- Review and update parameters as needed:
Review and Deploy
- Review the configuration changes
- Acknowledge any capabilities if prompted
- Click Update stack to begin the update process
The update process will maintain your existing resources (e.g., secrets, IAM roles) while deploying the new configuration. Monitor the stack events to track the update progress.
Deploy on Kubernetes
The datahub-executor-worker Helm chart provides a streamlined way to deploy Remote Executors on any Kubernetes cluster, including Amazon EKS and Google GKE.
- Registry Access Configuration
To access the private Acryl container registry, you'll need to work with your Acryl representative to set up the necessary permissions:
- For AWS EKS: Provide the IAM principal that will pull from the ECR repository
- For Google Cloud: Provide the cluster's IAM service account
- For other platforms: Contact Acryl for specific requirements
- Configure Secrets
Create the required secrets in your Kubernetes cluster:
# Create DataHub PAT secret (required)
# Generate token from Settings > Access Tokens in DataHub UI
kubectl create secret generic datahub-access-token-secret \
--from-literal=datahub-access-token-secret-key=<DATAHUB-ACCESS-TOKEN>
# Create source credentials (optional)
kubectl create secret generic datahub-secret-store \
--from-literal=REDSHIFT_PASSWORD=password \
--from-literal=SNOWFLAKE_PASSWORD=password
- Install Helm Chart
Add the Acryl Helm repository and install the chart:
# Add Helm repository
helm repo add acryl https://executor-helm.acryl.io
helm repo update
# Install the chart
helm install \
--set global.datahub.executor.pool_id="remote" \
--set global.datahub.gms.url="https://<your-company>.acryl.io/gms" \
--set image.tag=v0.3.1 \
acryl datahub-executor-worker
Required parameters:
global.datahub.executor.pool_id: Your Executor Pool IDglobal.datahub.gms.url: Your DataHub Cloud URL (must include/gms)image.tag: Acryl Remote Executor version
- Configure Secret Mounting (Optional)
Starting from DataHub Cloud v0.3.8.2, you can manage secrets using Kubernetes Secret CRDs. This enables runtime secret updates without executor restarts.
Create a Kubernetes secret:
# secret.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: datahub-secret-store
data:
REDSHIFT_PASSWORD: <base64-encoded-password>
SNOWFLAKE_PASSWORD: <base64-encoded-password>
Mount the secret in your values.yaml:
extraVolumes:
- name: datahub-secret-store
secret:
secretName: datahub-secret-store
extraVolumeMounts:
- mountPath: /mnt/secrets
name: datahub-secret-store
Secret Configuration:
- Default mount path:
/mnt/secrets(override withDATAHUB_EXECUTOR_FILE_SECRET_BASEDIR) - Default file size limit: 1MB (override with
DATAHUB_EXECUTOR_FILE_SECRET_MAXLEN) - Reference secrets in ingestion recipes using
${SECRET_NAME}syntax
Example ingestion recipe using mounted secrets:
source:
type: redshift
config:
host_port: '<redshift-host:port>'
username: connector_test
password: '${REDSHIFT_PASSWORD}'
# ... other configuration ...
For additional configuration options, refer to the values.yaml file in the Helm chart repository.
Once you have successfully deployed the Executor in your environment, DataHub will automatically begin reporting Executor Status in the UI:

Assigning Ingestion Sources to an Executor Pool
After you have created an Executor Pool and deployed the Executor within your environment, you are now ready to configure an Ingestion Source to run in that Pool.
- Navigate to Manage Data Sources in DataHub Cloud
- Edit an existing Source or click Create new source
- In the Finish Up step, expand the Advanced to select your desired Executor Pool

New Ingestion Sources will automatically use your designated Default Pool if you have assigned one. You can override this assignment when creating or editing an Ingestion Source at any time.
- Click Save & Run. The task should show as 'Running' if properly configured.

Advanced: Performance Settings and Task Weight-Based Queuing
Executors use a weight-based queuing system to manage resource allocation efficiently:
- Default Behavior: With 4 ingestion threads (default), each task gets a weight of 0.25, allowing up to 4 parallel tasks
- Resource-Intensive Tasks: Tasks can be assigned a higher weight (up to 1.0) to limit parallelism
- Queue Management: If the total weight of running tasks exceeds 1.0, new tasks are queued until capacity becomes available
- Priority Tasks: Setting a weight of 1.0 ensures exclusive resource access - the task will run alone until completion
The following environment variables can be configured to manage memory-intensive ingestion tasks, prevent resource contention, and ensure stable execution of resource-demanding processes:
DATAHUB_EXECUTOR_INGESTION_MAX_WORKERS(default: 4) - Maximum concurrent Ingestion tasksDATAHUB_EXECUTOR_MONITORS_MAX_WORKERS(default: 10) - Maximum concurrent Observe monitoring tasksEXECUTOR_TASK_MEMORY_LIMIT- Memory limit per task in kilobytes, configured per Ingestion Source under Extra Environment Variables. This setting helps prevent the executor's master process from being OOM-killed and protects against memory-leaking ingestion tasks. Example configuration:{"EXECUTOR_TASK_MEMORY_LIMIT": "128000000"}EXECUTOR_TASK_WEIGHT- Task weight for resource allocation, configured per Ingestion Source under Extra Environment Variables. By default, each task is assigned a weight of 1/MAX_THREADS (e.g., 0.25 with 4 threads). The total weight of concurrent tasks cannot exceed 1.0. Example configuration for a resource-intensive task:{"EXECUTOR_TASK_WEIGHT": "1.0"}
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Connection Failed
- Verify network connectivity
- Check DataHub URL configuration
- Validate access token
Secret Access Failed
- Confirm secret ARNs/names
- Check permissions
- Verify secret format
Container Failed to Start
- Check resource limits
- Verify registry access
- Review container logs
Frequently Asked Questions
Do AWS Secrets Manager secrets automatically update in the executor?
No. Secrets are wired into the executor container at deployment time. The ECS Task needs to be restarted when secrets change.
How can I verify successful deployment?
For ECS deployments, check AWS Console:
- Navigate to ECS > Cluster > Stack Name > Services > Logs
- Look for the log line:
Starting datahub executor worker
This indicates successful connection to DataHub Cloud.